- Home
- SUMMARY
- BY TEXTBOOK Apri sottomenù
-
BY TOPIC
Apri sottomenù
- S1 : Greenhouse effect
- S2 : Anthropogenic cause
- S3 : Future scenarios of temperature increases
- S4 : Impacts on Earth’s systems
- S5 : Impacts on economic and social systems
- E1 : Mitigation as a social dilemma
- E2 : Carbon pricing
- E3 : Discounting in reference to climate change
- E4 : Inequality in reference to climate change
- E5 : Social Cost of Carbon and IAMs
- E6 : Persistency & irreversibility in reference to climate change
- E7 : Climate decision-making under uncertainty
- E8 : Climate policies
- E9 : Behavioural issues in reference to climate change
- E10 : Adaptation and geoengineering
- SAMPLE LECTURE
- ABOUT US
S1 : Greenhouse effect
Any statement linking greenhouse gas emissions and the warming of the planet will be recorded in this section.
US-1-m
295
There have been efforts to address greenhouse gases [...] and slow global warming.
US-3-m
625
Now virtually the entire world is concerned about pollution. Carbon dioxide (CO2), which is primarily produced by burning fossil fuels, is a major contributor to global warming, damages marine life, and causes additional harm.
US-4-m
1043
One serious problem that the world will face in upcoming years is climate change. Science has conclusively shown that emissions of greenhouse gases are changing the earth’s climate. On a global scale, greenhouse gases trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere.
[...]
An accumulation of greenhouse gases caused by the use of fossil fuels has led to changes in the earth’s climate, known as climate change.
[...]
Greenhouse gases are gas emissions that trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere.
US-5-m
151
The United States should substantially increase its tax on gasoline, because doing so would lower gasoline consumption and thereby reduce dependence on imported oil and reduce the greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to global warming.
259
Most energy consumption uses fossil fuels and thus contributes to the emission of greenhouse gases and global warming.
689
The shift from coal to natural gas is an important step in reducing CO2 emissions and global warming.
694
Global warming is thought to result from the accumulation of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses (GHGs) in the atmosphere. (As the GHG concentration grows, more sunlight is absorbed into the atmosphere rather than being reflected away, causing an increase in average temperatures.)
697
By trapping sunlight, these higher GhG concentrations are likely to cause a significant increase in global mean temperatures in 50 years or so and could have severe environmental consequences.
US-6-m
47
Carbon dioxide emissions, which result when oil, coal, and natural gas are burned, have been identified as the primary cause of global climate change.
426
These gases act much like the glass in a greenhouse—allowing solar radiation to penetrate but then trapping it and increasing temperatures.
[...]
Greenhouse gases: gases such as carbon dioxide and methane whose atmospheric concentrations influence global climate by trapping solar radiation.
427
As atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases increase, the world is expected to become warmer, on average.
US-7-m
146
The burning of fossil fuels like oil and coal generates carbon dioxide, CO2, a “greenhouse gas” that most scientists believe contributes to global warming.
148
The burning of fossil fuels generates carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that can increase global warming.
164
Burning these fuels releases carbon dioxide, which accumulates in the atmosphere as a “greenhouse gas.” Greenhouse gases cause some of the heat released from the earth to be reflected back, increasing temperatures.
US-8-m
799
There is scientific consensus that without a significant reduction in the production of greenhouse gases, which engulf the atmosphere and lead to global warming, irreversible damage to the climate, ecosystems, and coastlines will result.
800
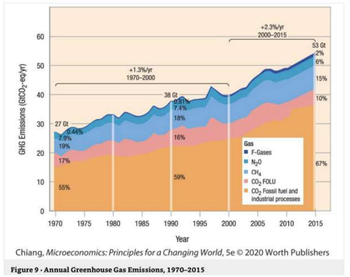
The primary causes of climate change are related to actions that emit greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases created largely by human activities include carbon dioxide (CO2) from fossil fuel and industrial processes, carbon dioxide (CO2) from forestry and other land use (FOLU), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases (F). Figure 9 shows both the global nominal rise in each of these greenhouse gases from 1970 to 2015 and the percentage of overall greenhouse gases that each source represents.
US-9-m
203
Point 1 reminds us that carbon released into the atmosphere contributes to climate change.
US-10-m
237
Consider global warming. Scientific evidence clearly links increasing amounts of CO2, (carbon dioxide) in the atmosphere and global warming.
US-12-m
196
Moreover, the burning of fossil fuels such as gasoline is widely believed to be the primary cause of global climate.
US-13-m
373
Burning coal generates substantial particulate and carbon dioxide emissions that may contribute to health problems as well as global warming.
US-16-m
6
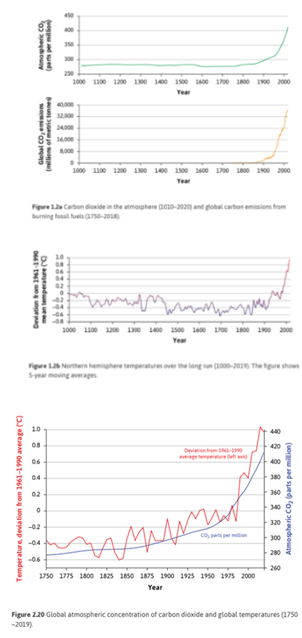
After having remained relatively unchanged for many centuries, increasing emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the air during the twentieth and twenty-first centuries have resulted in measurably larger amounts of CO2 in the earth’s atmosphere (Figure 1.2a) and brought about perceptible increases in the northern hemisphere’s average temperatures (Figure 1.2b)). Figure 1.2a also shows that CO2 emissions from fossil fuel consumption have risen dramatically since the late 1800s.
[...]
Since 1900, average temperatures have risen in response to increasingly high levels of greenhouse gas concentrations. These have mostly resulted from the CO2 emissions associated with the burning of fossil fuels. And in each year of the twenty-first century, the average temperature has been higher than at any time in the previous millennium.
91
Greenhouse gases such as CO2 allow incoming sunlight to pass through the atmosphere, but trap reflected heat on the earth, leading to increases in atmospheric temperatures and changes in climate.
US-2-M
344
There is broad scientific consensus that burning fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas—leads to increasing levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a type of greenhouse gas. Such gases trap the sun’s energy, raising the planet’s temperature, and lead to climate change, which, in turn, imposes high human, economic, and environmental costs.
347
The accumulation of greenhouse gases, a by-product of burning fossil fuels, has led to climate change, the raising of the earth’s temperature.
FR-2-m
299
Par exemple, William Pizer (2002) a fait des simulations concernant le dioxyde de carbone (CO2), le principal polluant atmosphérique impliqué dans l'effet de serre et le réchauffement climatique.
FR-4-m
226
Il est très complexe d’estimer l’effet moyen de l’émission d’une tonne de carbone sur le réchauffement climatique.
FR-4-M
308-309
Le principal gaz à effet de serre est le dioxyde de carbone (CO2). Une partie de l'énergie (sous forme de lumière) transmise par le Soleil à la Terre est absorbé par la Terre, l’autre partie étant réfléchie vers l'espace. Or, la quantité de CO2 dans l’atmosphère détermine l'importance de l'« effet de serre », et donc la part d'énergie absorbée et la part qui est réfléchie. Cette quantité absorbée est elle-même un déterminant majeur de la température globale de la planète. En l'absence totale dans l'atmosphère de dioxyde de carbone (et d'autres gaz à effets de serre), la quantité d'énergie absorbée serait trop faible, on estime que la température du globe serait d'environ -18 °C. À l'inverse, avec une trop grande quantité de CO2, dans l'atmosphère, la température augmente et conduit au réchauffement global.
[...]
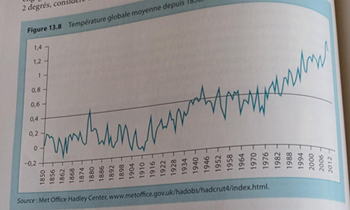
La figure 13.8 montre l'augmentation de la température moyenne depuis 1850, qui s'écarte de plus en plus de la moyenne correspondant à la période 1961-1990. La température a augmenté d'environ 1,2 °C depuis 1850, l'essentiel de l'augmentation ayant eu lieu depuis la fin des années 1970.
L'augmentation combinée des émissions de CO2 et de la température globale est un fait indéniable, que seuls contestent des excentriques (malheureusement, ils existent). Ce réchauffement climatique pose un problème majeur, et il faut réduire les émissions de CO2 pour le limiter.
312
Il est prouvé que la température moyenne mondiale a augmenté régulièrement et que cela est très probablement dû à l'augmentation des émissions de CO2. Jusqu'à présent, les progrès ont été insuffisants.
FR-7-M
53
L'effet de serre, c'est-à-dire le lien causal entre la concentration de certains gaz dans la couche d'ozone et la température à la surface de la terre, est connu depuis le xix siècle.
FR-2-B
148
Le développement durable implique une concertation internationale pour agir efficacement, et c'est particulièrement le cas en ce qui concerne le changement climatique puisque ses causes, l'émission des GES étant la principale, comme ses conséquences, telles que la montée du niveau des océans, sont mondiales.
FR-4-B
496
Ces problèmes, et notamment le dérèglement climatique lié principalement aux émissions de gaz à effet de serre se posent directement à l'échelle planétaire.
IN-2-M
46
As a matter of fact, it is the developed countries who in the past for achieving rapid industrial growth have contributed a lot to the emission of harmful gases such as carbon dioxide that have significantly contributed to the global warming affecting the welfare of the people of developing countries.