2GC what are they?
Second-generation carbons (2G-C)represent a wide range of carbon-based substances that differ in composition, structure, properties, and uses and have in common the technological process of production: they are obtained by pyrolysis of carbonaceous materials and possible mineral components.
Our economy produces several high-carbon-content flows like, e.g., agro-food and oil&gas. We want to transform these flows into high value added carbons.
We produce special and functionalized carbon-based materials (Second Generation Carbons) containing carbon of biological or fossil origin and mineral components (metals, alkalis, other inorganic components).
Second Generation Carbons as adsorbent materials (substitute for activated carbons):
- treatment of urban and industrial effluents with recovery of nutrients (P and N) and critical materials
- land and water remediation
- improvement of agricultural soil
- carbon sequestration and carbon credits
Second Generation Carbons for specific uses:
- batteries / accumulators / supercondensers
- CO2 recovery and management
Modeling:
- we integrate different types of models (mathematical, physical, bio-ecological, economic and social) for:
- the evaluation of environmental systems (e.g. soil quality)
- the storage of carbon in soils - carbon credits
- the diffusion of pollutants in groundwater
The lines of development include simulations, experiments and field observations.
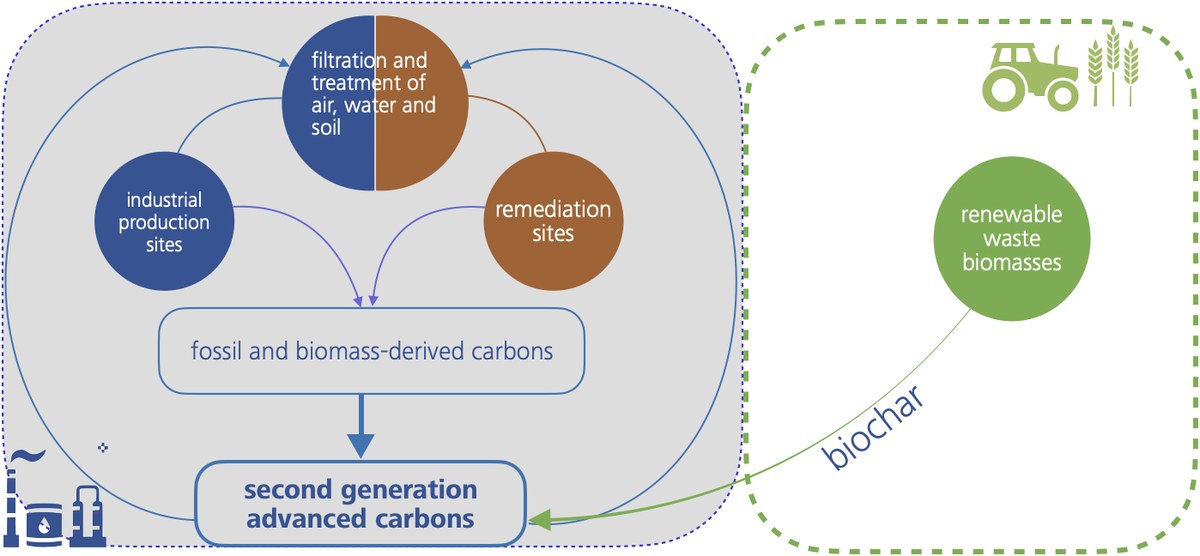
Second generation carbons derive from organic by-products or waste, containing carbon of biological origin, fossil carbon and mineral components (metals, alkalis and other inorganic components) for the preparation of replacement materials for activated carbon, materials used in filtration processes and materials for CO2 capture.