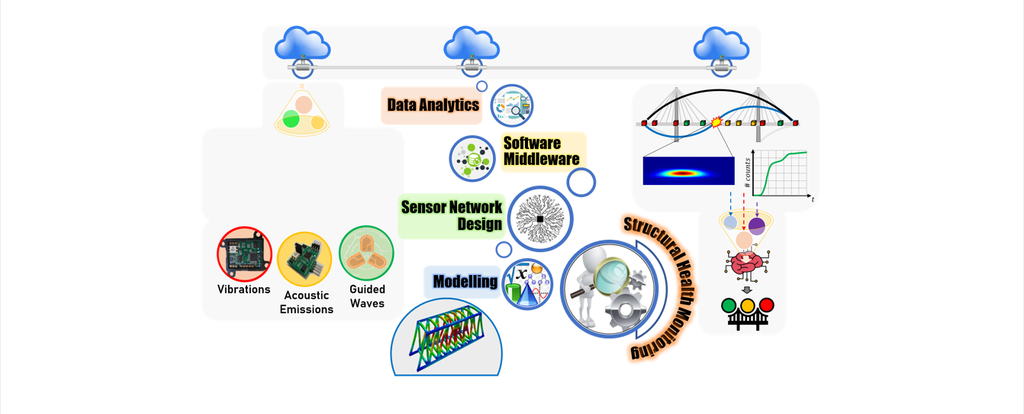
Sensor and Processing Techniques for Vibration-based SHM
Sensor-node for SHM
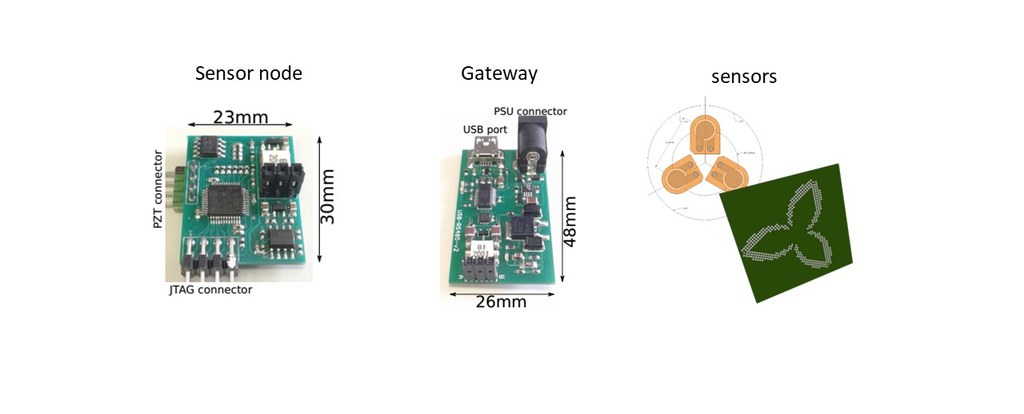
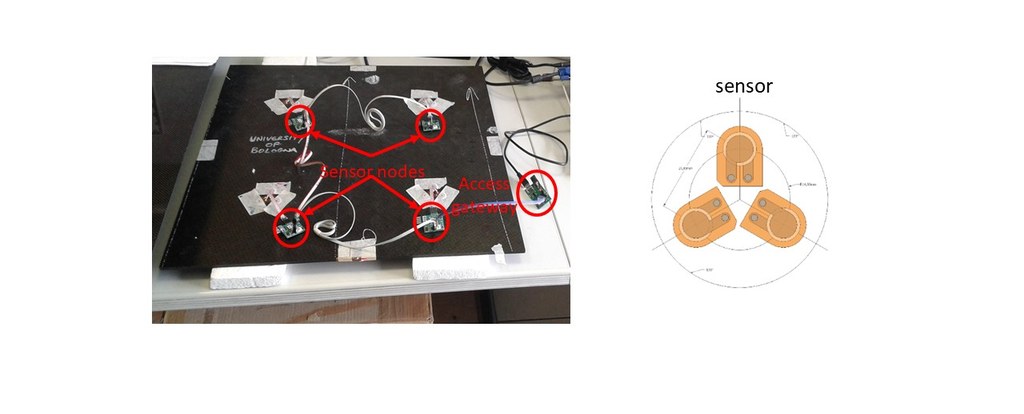
We propose an innovative, low-cost and low-weight Sensor Node (SN) which can yield fast deployable sensor networks for long–term and real–time acoustic emission (AE) and vibration (ACC) monitoring. Thanks to the interface and architecture of the developed system, Digital Signal Processing (DSP) functionalities were embedded in the proposed SN which are exploited for signal features extraction and signal characterization, compliant with a complete Structural Monitoring analysis. The on–board DSP strategy, performed in close proximity to the transducers at monitoring facility, permits to significantly minimize the sensitivity to external noise. This 'sensor-near' monitoring approach allows reducing drastically the volume of raw data to be processed and stored for NDT and SHM purposes.
References
- N. Testoni, F. Zonzini, A. Marzani, V. Scarponi, L. De Marchi, A Tilt Sensor Node Embedding a Data-Fusion Algorithm for Vibration-Based SHM, Electronics, 8(1), 45, 2019.
- N. Testoni, C. Aguzzi, V. Arditi, F. Zonzini, L. De Marchi, A. Marzani, T. Salmon Cinotti, A sensor network with embedded data processing and data-to-cloud capabilities for vibration based real-time SHM, Journal of Sensors, 2018, 2107679 (12 pages), 2018.
Graph Signal Processing
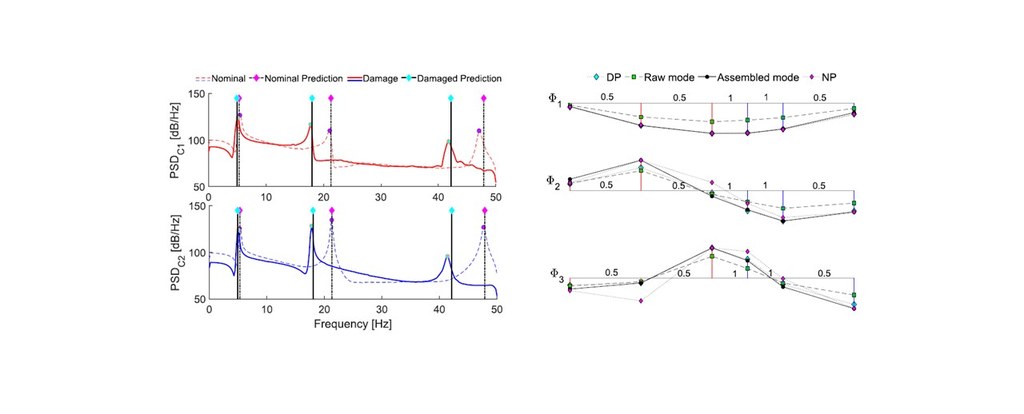
Signal processing techniques for inter- and intra- cluster data assembly are introduced to allow for a full-scale assessment of the structural integrity. The capability of graph signal processing (GSP) is adopted for the first time in vibration-based monitoring scenarios to capture the spatial relationship between acceleration data. Moreover, GSP eases the sensor deployment on large structures by exploiting a novel clustering scheme, which consists of unconventional and non-overlapped sensing configurations.
Experimental validation, conducted on a steel beam perturbed with additive mass, reveals high accuracy in damage detection tasks. Deviations in spectral content and mode shape envelopes are correctly revealed regardless of environmental factors and operational uncertainties. Additional key advantage of the implemented GSP architecture relies on its compliance with blind modal investigations, an approach that favours the implementation of autonomous smart monitoring systems.
References
- F. Zonzini, L. De Marchi, A. Girolami, D. Brunelli, A. Marzani, Cluster-based Vibration Analysis of Structures with Graph Signal Processing, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 68(4), 9037192, 3465-3474, 2021.
- F. Zonzini, C. Aguzzi, L. Gigli, L. Sciullo, N. Testoni, L. De Marchi, M. Di Felice, T. Salmon Cinotti, C. Mennuti, A. Marzani, Structural Health Monitoring and Prognostic of Industrial Plants and Civil Structures: A Sensor to Cloud Architecture, IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 23(9), 9289069, 21-27, 2020.
- F. Zonzini, M.M. Maltesta, D. Bogomolov, N. Testoni, A. Marzani, L. De Marchi. Vibration-based SHM with up-scalable and low-cost Sensor Networks, IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation & Measurement, 60 (10), 9044757, 7990-7998, 2020.