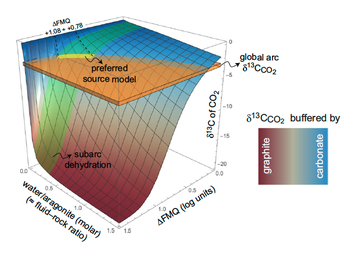
Great work done in the Milano experimental petrology lab by Simone Tumiati et al. The experiment revealed that the source of carbon being degassed at volcanic arcs is subjected organic carbon, whereas its carbon isotope signature is imposed by reequilibration with subjected carbonates. the carbon isotope signature of CO2 can be predicted by a mathematical model function of both fO2 and water-aragonite molar ratio.
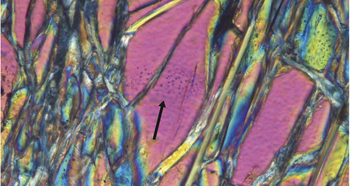
This papers documents high-pressure fluid-peridotite interactions leading to serpentinization, H2 genesis, and conversion of dissolved C into abiotic CH4 in the Appalachian subduction. This is the first paper of Antoine Boutier's PhD on the genesis and migration of deep CH4.
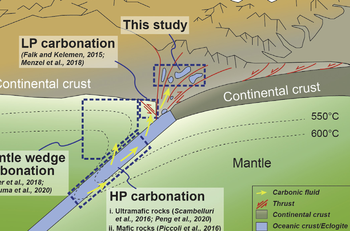
This paper presents new insights on processes of geological deep carbon storage in subduction zones through the process of retrograde carbonation of high-pressure rocks. This work was part of Han Hu's PhD based at Peking University, Beijing, China.
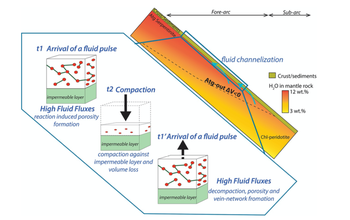
This study provides the first natural evidence for large-scale high-permeability channels in subducting slabs as indicated by km-scale metasomatic processes in Alpine Corsica, France.