Free Radicals Reactivity
Organic Free Radicals
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) is extensively employed in our laboratory for the characterized of neutral and charged organic free radicals.
Electronic properties, life times and reactivity of free radicals can be determined by using EPR. The analysis of complex EPR spectra is performed by comparison with theoretical simulations carried out by programs developed in our laboratory and based on Monte Carlo procedures.
The group has also developed an EPR method called radical equilibration electron paramagnetic resonance (REqEPR) which presently seems to guarantee the best accuracy between those described in the literature for the determination of bond dissociation enthalpies (BDE) of X-H bond.
Selected publications
- M. Lucarini, G. F. Pedulli, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 2106–2119.
Oxido-reductive radical processes
The aim of the project of this Research Unit is the development of new oxido-reductive radical processes of industrial and synthetic relevance, characterized by a low environmental and economic impact.
In particular we are involved in the design and employment of new N-hydroxyderivatives as key catalysts for the development of oxidative processes of organic derivatives, in the presence of air or as terminal economical "green" oxidants under mild conditions. The development of stereoselective oxidative processes is also one of the target of the project.
We are also involved in the development of reductive synthetic procedure based on free radicals avoiding highly toxic tin derivatives.
The work is done in collaboration with the group of Osvaldo Lanzalunga at the University of Rome
Selected publications
- G. A. DiLabio, P. Franchi, O. Lanzalunga, A. Lapi, F. Lucarini, M. Lucarini, M. Mazzonna, V. Kumar Prasad, B. Ticconi, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 6133
Polymer stabilization
Hindered amine stabilizers (HALS) are extensively used to protect polyolefins from photoxidation and thermoxidative degradation.
The mechanism of protection involves oxidation of the amines to nitroxide radicals, which by reaction with radicals from the polymer give rise to hydroxyl-amines and alkylated hydroxylamines. These, in turn, can regenerate the nitroxides, restarting the protective cycle many times before the additive, in its various oxidation forms, is completely depleted. The intermediate nitroxide radicals are very long lived species that can be easily detected by EPR spectroscopy (especially in a solid matrix as that of the host polymer). We have extensively used both conventional EPR and EPR-Imaging (EPRI) techniques by which the free radical distribution along the spatial coordinate coincident with the direction of the magnetic field can be determined. The joined use of EPR and EPRI provides information not only on the nature of the radical present in a given sample and on its concentration in the bulk, but also on its distribution at various depths of the sample. This information may be very important both in clarifying the mechanism of polymer stabilization as well as in the technological search of better additives or of mixtures of additives exhibiting a synergetic protective action for polymers.
The research is done in collaboration with BASF Italia, Pontecchio Marconi, BO
Selected publications
- M. Lucarini, G. F. Pedulli, M. V. Motyakin, S. Schlick “Electron spin resonance imaging of polymer degradation and stabilization”, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 331–340
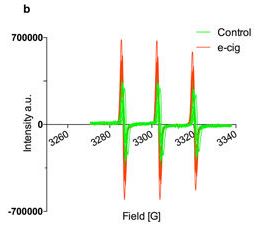
Free radicals in biology
Free radicals play an important role in many biological processes and their involvement in such processes can be checked by EPR. Because only paramagnetic species are detected by EPR, complex biological matrix can be investigated.
Selected publications
- D. Canistro et al. "E-cigarettes induce toxicological effects that can raise the cancer risk" Scientific Reports 2017, 7, Article number: 2028