
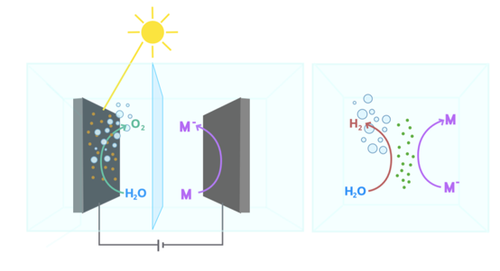
LEAF targets the design and development of a modular photoelectrochemical system for the decoupled production of solar fuels and implementation of a carbon-neutral energy landscape. The LEAF approach aims to decouple hydrogen and oxygen production in time and/or in space. This is realized by two steps: the first one consists of a phototelectrochemical cell where water oxidation is coupled to the reduction of a redox mediator (M). In step 2, the so-obtained reduced form of the redox mediator is used to drive water reduction.
The main advantages of the LEAF approaches compared to direct water splitting are:
(i) rate of the hydrogen evolution reaction not limited by the oxygen evolution reaction;
(ii) no mixing of hydrogen and oxygen gases by physical separation of the two processes;
(iii) operation under milder conditions, without interference by possible production of oxygen reactive species.
Department of Chemistry Ciamician - University of Bologna
Prof. Paola Ceroni - Prof. Francesco Paolucci
Department of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences - University of Ferrara
Department of Chemical Sciences- University of Catania
9th October 2024: Hydrogen Research Day - Bologna, results of the LEAF project were presented by Prof. Francesco Paolucci (invited oral presentation) and a pitch presentation delivered by Caterina Bellatreccia (PhD student under the supervision of Prof. Paola Ceroni)
27th September 2024: LEAF project was presented at the Research Night in Bologna, demonstrating the potentialities of artificial photosynthesis to a non-specialized audience
9th July 2024: LEAF meeting at the University of Ferrara to discuss the project development
17th January 2024: kick-off meeting
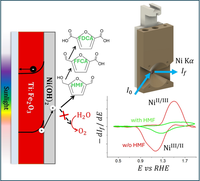
Nickel‐Based Cocatalysts on Titanium‐Doped Hematite Empower Direct Photoelectrochemical Valorisation of 5‐Hydroxymethylfurfural
by I. Carrai, R. Mazzaro, C. Bellatreccia, A. Piccioni, M. Salvi, S. Grandi, S. Caramori, P. Ceroni, L. Pasquini